Networking-interview-questions-answers
Q1. What are the two types of transmission technology available?
Ans. The two types of transmission technology are – broadcast and point-to-point.
Q2. What is a ‘subnet’?
Ans. A ‘subnet’ is a generic term for a section of an extensive network, usually separated by a bridge or a router.
Q3. What is DNS?
Ans. The Domain Name System (DNS) is a central part of the internet, providing a way to match names (a website you’re seeking) to numbers (the address for the website). Anything connected to the internet – laptops, tablets, mobile phones, and websites – has an Internet Protocol (IP) address made up of numbers.
Q4. Explain ‘hidden shares’.
Ans. A hidden or administrative share is a network share that is not visible when viewing another computer’s shares.
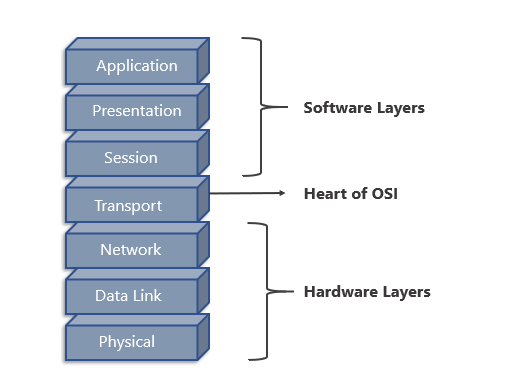
Q5. How many layers are there in the OSI model? Name them
Ans. There are seven layers – physical, data link, network, transport, session, presentation, and application.
Also Read>> Cloud Computing: The good and the bad!!
Q6. What is a ‘client’ and ‘server’ in a network?
Ans. Clients and servers are separate logical entities that work together over a network to accomplish a task.
Q7. What are the different ways to exchange data?
Ans. Following are the different ways to exchange data:
Simplex
Half-duplex
Full-duplex
Also, Read>> Big Data and IoT: Making The Connection
Q8. What is a ‘frame relay’ and in which layer does it operate?
Ans. A frame relay is a packet-switching technology. It operates in the data link layer.
GET CCNP CERTIFIED NOW>>
Q9. What is a MAC address?
Ans. A MAC (Media Access Control) address is the 48-bit hardware address of a LAN card and is usually stored in the ROM of the network adapter card and is unique.
Q10. What are the perquisites to configure a server?
Ans. Perquisites to configure a server are:
LAN card should be connected
Root (partition on which window is installed) should be in NTFS format
A server should be configured with a static IP address
Q11. What is ‘beaconing’?
Ans. Beaconing is the process that allows a network to self-repair network problems.
Q12. Differentiate between ‘attenuation’, ‘distortion’, and ‘noise’.
Ans. When a signal travels through a medium, it loses some of its energy due to the resistance of the medium. This loss of energy is called attenuation.
When a signal travels through a medium from one point to another, it may change the form or shape of the signal. This is known as distortion.
Noise is unwanted electrical or electromagnetic energy that degrades the quality of signals and data.
GET CCNA CERTIFIED NOW>>
Q13. What is an IP address?
Ans. An Internet Protocol address (IP address) is a numerical label assigned to each device (e.g., computer, printer) participating in a computer network that uses the Internet Protocol for communication.
Also, Read>> Top Network Engineer Interview Questions & Answers.
Q14. Differentiate between a ‘bit rate’ and ‘baud rate’.
Ans. A bit rate is the number of bits transmitted during one second, whereas, baud rate refers to the number of signal units per second that are required to represent those bits.
Baud rate = bit rate / N, where N is the no. of bits represented by each signal shift.
Q15. What is ‘bandwidth’?
Ans. The limited range of frequency of signals that a line can carry is called the bandwidth.
Q16. What is Project 802?
Ans. It is a project started by IEEE to set standards to enable intercommunication between equipment from a variety of manufacturers.
Q17. What is ICMP?
Ans. ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol) is a network layer protocol of the TCP/IP suite used by hosts and gateways to send notification of datagram problems back to the sender.
Q18. What are the major types of networks?
Ans. Following are the major types of networks:
Server-based network
Peer-to-peer network
Also Read>> Cisco Certifications: CCNA Vs. CCNP
Q19. What are the important topologies for networks?
Ans. There are three essential topologies – Star, Bus, and Ring.
Q20. Differentiate between static IP addressing and dynamic IP addressing.
Ans. In static IP addressing, a computer (or another device) is always configured to use the same IP address, whereas in dynamic IP addressing, the IP address can change periodically and is managed by a centralised network service
Q21. What is a LAN?
Ans. LAN stands for Local Area Network and it refers to the connection between computers and other network devices, located in proximity to each other.
Q22. What are routers?
Ans. Routers connect two or more network segments. These intelligent network devices store information in its routing table such as paths, hops, and bottlenecks. They determine the most accurate data transfer paths and operate in Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) Network Layer.
Q23. What is data encapsulation?
Ans. Data encapsulation is the process of breaking down information into smaller, manageable chunks before their transmission across the network.
Q24. What is a VPN?
Ans. VPN stands for Virtual Private Network. This is a connection method for adding security and privacy to private and public networks, such as Wi-Fi Hotspots and the Internet. VPNs help in establishing a secure dial-up connection to a remote server.
Q25. How can you secure a computer network?
Ans. There are several ways to achieve this.
Install a reliable and updated antivirus program across the network
Ensure firewalls are setup and configured properly
Monitor firewall performance
User authentication
Update passwords regularly, every quarter
Create a virtual private network (VPN)
Q26. What are proxy servers and how do they protect computer networks?
Ans. Proxy servers prevent external users from identifying the IP addresses of an internal network. They make a network virtually invisible to external users, who cannot identify the physical location of a network without knowledge of the correct IP address.
Q27. What are Nodes and Links?
Ans. Nodes – Devices or data points on a larger network are known as nodes. They are individual parts of a larger data structure and contain data. They also link other nodes.
Links- A link is the physical and logical network component for interconnecting hosts or nodes in a network. It is a physical communication medium such as coaxial cable or optical fiber.
Q28. What is SLIP?
Ans. SLIP or Serial Line Interface Protocol was developed during the early UNIX days and it is used for remote access.
Q29. What is TCP/IP?
Ans. TCP/IP is the short form of the Transmission Control Protocol / Internet Protocol. It is a set of protocol layers designed to facilitate data exchange on heterogeneous networks.
Q30. What common software problems lead to network defects?
Ans. It can be any or a combination of –
Application conflicts
Client-server problems
Configuration error
Protocol mismatch
Security issues
User policy & rights issues
Q31. What is a client/server network?
Ans. In a client/server network, one or more computers act as servers. Servers offer a centralized repository of resources such as printers and files. The client refers to a workstation that has access to the server.
Q32. Describe networking.
Ans. Networking facilitates data communication between computers and peripherals, and it is done through wired cabling or wireless links.
Q33. Why is encryption on a network necessary?
Ans. Encryption is the process of changing data from its original readable format to an unreadable format, thus ensuring network security. It requires the user to use a secret key or password to decrypt the data.
Q34. What are the types of errors?
Ans. There are two categories of errors –
Single-bit error – one-bit error per data unit
Burst error – Two or more bits errors per data unit
Q35. What is a client-server model?
Ans. The client-server model is a distributed communication framework for network processes. This framework is distributed among service requestors, clients and service providers.
Q36. What is TELNET?
Ans. TELNET is a client-service protocol on the internet or local area network, allowing a user to log on to a remote device and have access to it. Technically, it is a bidirectional interactive text-oriented communication facility, which uses a virtual terminal connection.
You probably now have a good idea of the type of questions that can be asked in a hardware and networking interview. Still, you need to be prepared to answer other kinds of questions that will test your interpersonal, business, or methodology skills.
If you are someone who has recently started your career in networking, you can think of enhancing your skills and getting a stamp for it via a professional certification course in hardware and networking. Naukri Learning offers a comprehensive range of such courses to help you get certified for various techniques and skills needed to be an expert in the field.
Add on questions – 2
Be prepared for some specific networking interview questions too. Here are some more.
Q37.What is RIP?
Ans. It is the abbreviation for Routing Information Protocol. It is a simple protocol that exchanges information between the routers.
Q38.What is half-duplex?
Ans. It is the mode of communication between two devices. Here the data flows bi-directionally but simultaneously. A perfect example of a half-duplex is a walkie-talkie.
Q39.What is full-duplex?
Ans. This is also a mode of communication between two devices and the data flow is bi-directional too, but the flow is simultaneous. Example – telephone.
Q40.What is netstat?
Ans. It is a command-line utility program that provides information about the current Transmission Control Protocol /Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) settings of a connection.
Q41.What is a peer-peer process?
Ans. The processes on each machine that communicate at a given layer are called the peer-peer process.
Q42.What is anonymous FTP?
Ans. With the help of an anonymous FTP, users can be granted access to files in public servers. Users can log in as anonymous guests, thus the name.
Q43.Can you explain NAT?
Ans. It stands for Network Address Translation and is a protocol that allows a network device, usually a firewall, to assign a public address to a computer/s inside a private network.
Q44.Can you tell me the main elements of a protocol?
Ans. This is among the very commonly asked networking interview questions. Your reply should be –
There are three main elements of a protocol –
Syntax: It refers to the structure or format of the data and their order of presentation.
Semantics: It specifies the meaning of each section of bits.
Timing: Timing refers to two characteristics, which include the timing of data sending and the speed of data sending.
Q45.What is NIC?
Ans. NIC is the abbreviation for Network Interface Card. It is a peripheral card with electronic circuitry. It is attached to a PC and connects it to a network. NIC has its own MAC address and this identifies a PC on the network.
Q46.What is the difference between Communication and Transmission?
Ans. Transmission – A process of sending and receiving data between source and destination, in only one way. It is regarded as the physical movement of data.
Communication – A process of sending and receiving data between source and destination, in both ways.
Q47.How many layers does TCP/IP have?
Ans. TCP/IP has four layers –
Network Layer
Internet Layer
Transport Layer
Application Layer
Q48.Explain NOS.
Ans. Short form for Network Operating System. Specialized software that provides connectivity to a computer such that it can communicate with other computers and devices on a network.
Q49.What is IDEA?
Ans. IDEA is the abbreviation for International Data Encryption Algorithm. It is the replacement for the Data Encryption Standard (DES).
Q50.What is ASCII?
Ans. American Standard Code for Information Interchange.
Q51.What is Brouter?
Ans. Brouter is a device that functions as both a bridge and a router. It forwards data within the networks and also routes data to individual systems in a network.
Q52.How would you differentiate between Firewall and Antivirus?
Ans. Both are security applications used in networking.
A firewall prevents unauthorized access in private networks as intranets. However, it does not protect against virus, spyware, or adware.
An antivirus is a software that protects a computer from any malicious software, virus, spyware, or adware.
Q53.How will you recover data from a Virus-infected system?
Ans. We will install an OS and updated antivirus in a system that is free of any viruses, and then connect the hard drive of the infected system as a secondary drive. The hard drive will then be scanned and cleaned. Data can now be copied into the system.
Q 54. What is ipconfig?
Ans. An acronym for Internet Protocol Configuration, Ipconfig is used on Microsoft Windows to view and configure the network interface. It displays all TCP/IP network summary information available on a network and helps to modify the DHCP protocol and DNS settings.
Q 55. What is ifconfig?
Ans. It is an acronym for Interface Configuration and is used on Linux, Mac, and UNIX operating systems. ifconfig configures and controls the TCP/IP network interface parameters from Command Line Interface while allowing the user to check the IP addresses of these network interfaces.
Q 56. What is the semantic gap?
Ans. A semantic gap is a difference between high-level programming sets in various computer languages and the simple computing instructions used by microprocessors.
Q 57. What is the difference between a Domain and a Workgroup?
Ans. The main difference is where do the computer networks belong to. If it is a home network, then computers will be a part of a workgroup, and if it’s a workplace network, then the computers will be a part of a domain.
Q 58. What Is NVT?
Ans. NVT stands for Network Virtual Terminal and is a representation of a primary terminal. It is used at the start of a Telnet session.
Q 59. What Is BGP?
Ans. BGP or Border Gateway Protocol is a protocol used to transfer data and information between different host gateways or autonomous systems.
Q 60. What is Round Trip Time?
Ans. Round Trip Time or RTT is the time taken to send a message from one end of a network to the other and back.
Q 61. What is 127.0.0.1 and localhost?
Ans. Localhost is the standard hostname given to the machine, and it is represented by the IP address 127.0.0.1. Therefore, we can say that 127.0.0.1 and localhost are the same thing.
Q 62. Which are the most typical functional units of the client/server applications?
Ans. The most typical functional units of the client/server applications are –
Presentation logic or user interface (e.g., ATMs)
Business logic (e.g., Account balance enquiry)
Data (e.g., Bank account records)
Q 63. What are the Triggers?
Ans. Triggers are event-driven specialized procedures and are managed by database management systems. It is capable of performing complex actions and use the procedural languages full throttle.
Q 64. What is a Gateway?
Ans. Gateway is a hardware device that is connected to two or more networks. It may be a router, firewall, server, or any other similar device, and is capable of regulating traffic in the network.
Q 65. Is there a difference between a gateway and a router?
Ans. A gateway sends the data between two dissimilar networks, while a router sends the data between two similar networks.
Q 66. Explain 10Base-T.
Ans. 10Base-T specifies data transfer rate, i.e., 10Mbps. Here the usage of the term ‘Base’ defines ‘Baseband’ and not ‘Broadband’. T denotes the type of cable, which is a twisted pair.
Q 67. Name the user support layers
Ans. There are three types of user support layers –
Session Layer
Presentation Layer and
Application Layer
Q 68. What is Piggy Backing?
Ans. It is the process of gaining access to a restricted communications channel by using an already established session by another user. This technique is known to improve the efficiency of the bidirectional protocols.
Q 69. What is asynchronous transmission?
Ans. It is a serial mode of transmission. It is the process of data transmission, where every character is a self-contained unit. Each character in asynchronous transmission has its start and stop bits, along with an uneven interval between them.
Q 70. What is synchronous transmission?
Ans. Synchronous transmission refers to continuous data streaming in the form of signals, accompanied by regular timing signals. These signals are generated by the external clocking mechanism and ensure that senders and receivers are in synchrony.
Q 71. What are the different types of transmission media?
Ans. Transmission media has two broad types –
Guided media (wired)
Unguided media (wireless)
Q 72. What is Process Sigma?
Ans. Process Sigma measures the frequency of a task that is performed without any error. It is expressed as a number of standard deviations on a normal distribution.
Q 73. What is FMEA?
Ans. Failure Mode Effect and Analysis or FMEA is a qualitative and systematic tool to identify potential failure modes in a system, the reasons, and their effects.
Q 74. What is the backbone network?
Ans. It refers to a centralized infrastructure for distributing different routes and data to various networks. Backbone networks connect LANs and WANs.
Q 75. What is OSPF?
Ans. OSPF is an abbreviation for Open Shortest Path First. It is a routing protocol that uses a link-state routing (LSR) algorithm to find out the best possible path for data exchange.
Q 76. Mention what is the range of addresses in the classes of internet addresses?
Ans. Following are the five different ranges of addresses in the classes of the internet:
Class A: 0.0.0.0 – 127.255.255.255
Class B: 128.0.0.0 – 191.255.255.255
Class C: 192.0.0.0 – 223.255.255.255
Class D: 224.0.0.0 – 239.255.255.255
Class E: 240.0.0.0 – 247.255.255.255
Q 77. Explain what the Datalink protocols are?
Ans. Datalink protocols are defined as the sets of requirements used to implement the data link layer. There are the following categories of Data Link protocols:
Synchronous Protocols
Asynchronous Protocols
Bit Oriented protocols
Character Oriented Protocols
Q 78. Mention the responsibilities of the Network Layer?
Ans. The Network Layer is liable for the source to destination delivery of packets across different networks or links.
Routing
Logical Addressing
Q 79. Name the access method used in 1000BaseTX network?
Ans. CSMA/CD access method is used in 1000BaseTX network.
Q 80. Mention the different types of links used to build a computer network?
Ans. Following are the different types of links used to build a computer network:
Cables
Wireless Links
Last-Mile Links
Leased Lines
Q 81. Mention the types of wires used for data transmission in UTP cable?
Ans. There are four types of wires used for data transmission in UTP cable, which are wire 1, 2, 3, and 6. Where wires 1 and 2 are used to transmit the data while wires 3 and 6 are used to receive the data.
Q 82. Can we use RG59 and RG6 cables in a computer network?
Ans. RG59 and RG6 cables are not used in the computer network. These cables are made for the cable TV network.
Q 83. Describe what 10Base2 stands for?
Ans. In networking, 10Base2 architecture is divided in three-strand where 10 stands for speed, Base stands for Baseband transmission, and 2 stands for 200 meters.
Q 84. Name the cable used in the 10BaseFL network?
Ans. Fiber optical cable is the cable used in the 10BaseFL network.
Q 85. Why is IP protocol deliberated as a connectionless protocol?
Ans. An IP protocol is deliberated as a connectionless protocol because it does not build up a connection before sending data to the endpoint.
Q 86. How many can network segments be populated in 10Base2?
Ans. The maximum three network segments can be populated in 10Base2.
Q 87. Explain what the point-to-point protocol is?
Ans. A communications protocol is used to connect computers to remote networking services, including Internet service providers.
Q 88. Mention what NIC stands for?
Ans. The NIC stands for the network interface controller.
Q 89. Mention any five applications which use TCP port.
Ans. Following are the five application which uses TCP port:
FTP
POP
SSH
SMTP
Telnet
Q 90. Explain what the 5-4-3 rule is? Mention in which architecture it is used?
Ans. In 5-4-3 rule, there are a maximum of five segments in a network that are connected with four repeaters. It is used in 10Base2 and 10Base5 Ethernet architectures. In this rule, only three segments can be populated with nodes.
You probably now have a good idea of the type of networking interview questions that can be asked in a hardware and networking interview. Still, you need to be prepared to answer other types of interview questions that will test your interpersonal, business, or methodology skills.
=================================================
Q1. Differentiate between a router, a hub, and a switch.
Q2. What is a link?
Q3. What do you mean by a Node?
Q4. What does a backbone network mean?
Q5. What is Network Topology?
Q6. Explain what is LAN?
Q7. What are Routers?
Q8. What is a Point-to-Point Network?
Q9. What is OSI Model?
Q10. Give a brief about each layer in the OSI Model.
Q1. Differentiate between a router, a hub, and a switch.
| HUB | SWITCH | ROUTER |
| Connects two or more Ethernet devices | Connects two or more LAN devices | Can connect devices or a LAN and WAN |
| Does not perform filtering | Filters packets before forwarding them | Highly configured to filter and send packets |
| Least intelligent, least expensive and least complex | Similar to a hub, but more effective | Extremely smart and complex |
Q2. What is a link?
A link basically is the connection between two or more computers or devices. It can be anything depending on whether it is a physical connection or a wireless one. Physical links include cables, hubs, switches, etc and wireless links wireless access points, routers, etc.
Q3. What do you mean by a Node?
The point of intersection in a network is called a Node. Nodes can send or receive data/ information within a network. For example, if two computers are connected to form a network, there are 2 nodes in that network. Similarly, in case there are computers, there will be three nodes and so on. It is not necessary for a node to be a computer, it can be any communicating device such as a printer, servers, modems, etc.
Q4. What does a backbone network mean?
In any system, backbone is the most principle component that supports all other components. Similarly, in networking, a Backbone Network is a Network that interconnects various parts of the network to which it belongs and has a high capacity connectivity infrastructure.
Q5. What is Network Topology?
The physical layout of the computer network is called as Network Topology. It gives the design of how all the devices are connected in a network.
| Type | Description |
| Bus Topology | All the devices share a common communication line |
| Star Topology | All nodes are connected to a central hub device |
| Ring Topology | Each node connects to exactly two other nodes |
| Mesh Topology | Each node is connected to one or more nodes |
| Tree Topology (Hierarchical Topology) | Similar to star topology and inherits the bus topology |
| Daisy Chain Topology | All nodes are connected linearly |
| Hybrid Topology | Nodes are connected in more than one topology styles |
| Point-to-Point Topology | Connects two hosts such as computers, servers, etc |
Q6. Explain what is LAN?
A LAN or Local Area Network the network between devices that are located within a small physical location. It can be either wireless or wired. One LAN differs from another based on the following factors:
- Topology: The arrangement of nodes within the network
- Protocol: Refer to the rules for the transfer of data
- Media: These devices can be connected using optic fibers, twisted-pair wires, etc
Q7. What are Routers?
A router is some device that transfers the data packets within a network. It basically performs the traffic directing functions within a network. A data packet can be anything such as an email, a web page, etc. Routers are located at the place where two or more networks meet or the gateways.
Routers can either be stand-alone devices or virtual. Stand-alone routers are traditional devices where as virtual routers are actually softwares that act like physical ones.
Q8. What is a Point-to-Point Network?
A Point-to-Point network refers to a physical connection between two nodes. It can be between any device of a network such as a computer, printer, etc.
For example, as you can see in the above diagram, all the nodes are connected to each other i.e Device 1 is connected to Device 2 and Device 3 , Device 2 is connected to Device 3 and Device 1 and Device 3 is connected to Device 2 and Device 1 using physical links.
Q9. What is OSI Model?
OSI stands for Open Systems Interconnection. It is a conceptual model that standardizes communication functions of telecommunication. It has 7 layers which are:
- Physical Layer
- Data Link Layer
- Network Layer
- Transport Layer
- Session Layer
- Presentation Layer
- Application Layer
Q10. Give a brief about each layer in the OSI Model.
| Layer Name | Protocol | Description |
| Physical Layer | Symbol | Transfers raw bits of data over a physical link |
| Data Link Layer | Frame | Reliable transmission of data frames between nodes connected by the physical layer |
| Network Layer | Packet | Structures and manages a network with multiple nodes including addressing, routing and traffic control |
| Transport Layer | Segment, Datagram | Reliable Transmission of data packets between the different points of a network |
| Session Layer | Data | Manages the communication sessions |
| Presentation Layer | Data | Transmission of data between the service device and the application |
| Application Layer | Data | Specifies the shared communication protocols and the interface methods |
Q11. What do you mean by anonymous FTP?
An anonymous FTP is a way of allowing a user to access data that is public. The user does not need to identify himself to the server and has to log in as anonymous.
So in case you are asked to use anonymous ftp, make sure you add “anonymous” in place of your user id. Anonymous FTPs are very effective while distributing large files to a lot of people, without having to give huge numbers of usernames and password combinations.
Q12. What is the meaning of Network?
A network is a connection between different devices. These devices communicate with each other using physical or wireless connections. Physical connections include twisted pair cables, optic fibers, and coaxial cables..wireless networks can be established with the help of waves such as radio waves infrared waves and microwaves
Networks basically serve many purposes such as:
- Sharing hardware devices such as printers, input devices, etc
- Help in communications in many ways such as audios videos emails messages etc
- Help in sharing data and information using virtual devices
- They also help sharing softwares that are installed on other devices
Q13. What do you mean by a Subnet Mask?
A Subnet Mask is the number describing the range of IP addresses that can be used within a network. They are used to assign subnetworks or subnets. These subnetworks are various LAN’s connected to the internet.
This Subnet mask is basically a 32-bit number and it masks the IP address and then divides the IP address into two parts i.e the network address and the host address. Subnet Masks are created by setting all the network bits to “1” and all the host bits to “0”s. There are two network addresses that cannot be assigned to any host on the network i.e The “0” and “255” which are assigned to network and to the broadcast address, and this is why they cannot be assigned to any host.
Q14. Give a brief description of the TCP/ IP Model.
The TCP/ IP Model is a compressed version of the OSI Model. This Model contains 4 layers unlike the OSI Model which are:
- Process(Application Layer)
- Host-to-Host(Transport Layer)
- Internet Layer (Network Layer)
- Network Access(Combination of Physical and Data Link Layer)
Q15. What is the difference between the OSI Model and TCP/ IP Model?
| TCP/ IP Model | OSI Model |
Has four layers | Has seven layers |
More reliable | Less reliable |
No strict boundaries | Has strict boundaries |
Horizontal Approach | Vertical Approach |
Q16. What is a UTP cable?
A UTP cable is a 100 ohms cable made up of copper. It consists of 2-1800 unshielded twisted pairs that are surrounded by a non-metallic case. These twists provide immunity to electrical noise and EMI.
Q17. What is the maximum length allowed for a UTP cable?
The maximum length allowed for a UTP cable is 100m. This includes 90 m of solid cabling and 10m of standard patch cable.
Q18. Explain what is HTTP and which port does it use?
HTTP or HyperText Transfer Protocol allows communication over the Internet. This protocol basically defines how messages are to be transmitted and formatted over the world wide web. HTTP is a TCP/ IP protocol and it uses the port number 80.
Features of HTTP Protocol:
- It is connection-less
- Does not depend on the type of connecting media
- Stateless
Q19. What is NAT?
NAT stands for Network Address Translation. It deals with remapping one IP Address space with another by changing the IP headers of the packets that are being transmitted across a traffic routing device.
Q20. What is TCP?
TCP or Transmission Control Protocol is a connection-oriented protocol that establishes and maintains a connection between communicating devices until both of them are done exchanging messages. This protocol determines how application data can be broken down into packets that can be delivered over a network. It also sends and receives packets to and from the network layer and is in charge of flow control, etc.
Q21. Give a brief explanation about UDP?
UDP or the User Datagram Protocol is used to create a low-latency and loss-tolerating communications between applications connected over the internet. UDP enables process-to-process communication and communicates via datagrams or messages.
Q22. Differentiate between TCP and UDP.
| Factor of comparison | TCP | UDP |
Connection | Connection made before application messages are exchanged | Connection not made before application messages are exchanged |
Use | For applications needing more reliability and less speed | For applications needing more speedy and less reliability |
Use by Protocols of the Application Layer | File transfer, e-mail, etc | Multimedia, DNS |
Reliability | Messages will be delivered in order and without errors | No guarantee that the messages will be delivered in order and without errors |
Data Segments | Data segments rearranged in required order | All segments are independent, therefore has no inherent order specification |
Acknowledgment | ACK is received | ACK is not received |
Flow Control | Has the congestion control mechanism | No flow control option |
Check for Errors | Resends erroneous segments | Discards Erroneous segments |
Q23. What is RIP?
RIP (Routing Information Protocol) is a dynamic routing protocol. It makes use of hop count as its primary metric to find the best path between the source and the destination. It works in the application layer and has an AD (Administrative Distance) value of 120.
Q24. Explain what is a firewall?
A firewall is a network security system which is used to monitor and control the network traffic based on some predefined rules. Firewalls are the first line of defense and establish barriers between the internal and external networks in order to avoid attack from untrusted external networks. Firewalls can be either hardware, software or sometimes both.
Q25. Explain what is NOS?
A Network Operating System (NOS) is an Operating System that is designed to support workstations, databases, personal computers, etc over a network. Some examples of NOS are MAC OS X, Linux, Windows Server 2008, etc. These Operating Systems provide various functionalities such as processor support, multiprocessing support, authentication, Web services, etc.
Q26. Explain what is Denial of Service (DoS)?
Denial of Service (DoS) is a kind of attack that prevents a legitimate user from accessing data over a network by a hacker or an attacker. The attacker floods the server with unnecessary requests in order to overload the server thereby preventing the legitimate users from accessing its services.
Q27. What is the full form of ASCII?
ASCII stands for American Standard Code for Information Interchange. It is a character encoding standard used in the electronic communication field. The ASCII codes basically represent text.
Q28. What is IEEE?
IEEE stands for Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineer. It is the world’s largest technical professional society and is devoted to advancing innovation and technological excellence.
Q29. What is a MAC address and why is it required?
MAC or Media Access Control address is a computer’s unique number assigned to a Network Interface Controller (NIC). It is a 48-bit number that identifies each device on a network and is also referred to as the physical address. MAC addresses are used as a network address for communications within a network such as an Ethernet, Wi-Fi, etc.
Q30. What is piggybacking?
During transmission of data packets in two-way communication, the receiver sends an acknowledgment (control frame or ACK) to the receiver after receiving the data packets. However, the receiver does not send the acknowledgment immediately, but, waits until its network layer passes in the next data packet. Then, the ACK is attached to the outgoing data frame. This process of delaying the ACK and attaching it to the next outgoing data frame is known as piggybacking.
Q31. Explain what is DNS?
DNS or Domain Name System is a naming system for devices connected over the internet. It is a hierarchical and decentralized system that translates domain names to the numerical IP Addresses which is required to identify and locate devices based on the underlying protocols.
All devices connected to the internet have unique IP addresses which are used to locate them on the network. The process involves conversion on hostnames into IP addresses. For example, in case the user wants to load some web page (xyz.com), this hostname is converted into an IP address that can be understood by the computer in order to load that web page.
Q32. Differentiate between Domain and a Workgroup.
| Domain | Workgroup |
Has one or more computer acting as a server | All computers are peers |
Has a centralized database | Each computer has its own database |
Computers can be on different LANs | All computers are on the same LAN |
Q33. What is OSPF?
OSPF stands for Open Shortest Path First. It is basically a routing protocol that is used to find the best path for packets that are being transmitted over interconnected networks.
Q34. What is Round Trip Time?
Round Trip Time or Round Trip Delay Time refers to the time taken for a signal to be sent and the ACK of that signal to be received.
Q35. What is DHCP?
DHCP or Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol is a network management protocol. It is used on the UDP/IP networks and it automatically assigns IP addresses to the devices on the network. This, in turn, reduces the need of a network admin to manually assign IP addresses thereby reducing errors.
Q36. Briefly explain what is ICMP?
ICMP stands for Internet Control Message Protocol and is a part of the Internet Protocol Suite. It is basically a supporting protocol to the Internet protocol and is used to send error messages and information regarding the success or failure of communication with another IP address. For example, if a service is not available an error is reported.
Q37. What is a Ping?
A ping is a computer program that is used to test the reachability of a host and check if can accept requests on an IP network. It works by sending an ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol) Echo to some computer on the network and waits for a reply from it. It can also be used for troubleshooting.
Q38. What are the advantages of optic fibers?
Optic fibers have a number of advantages such as:
- Greater bandwidth than other metal cables
- Low power loss allows longer transmission distances
- Optic cables are immune to electromagnetic interference
- Lesser production rates
- Thin and light
- The optical fiber cable is difficult to tap
Q39. What is a client/ server network?
A client/ server network is a network where one computer behaves as a server to the other computers. The server is usually more powerful than the clients and serves the clients.
Q40. In a network that contains two servers and twenty workstations, where is the best place to install an Anti-virus program?
The best solution is to install anti-virus on all the computers in the network. This will protect each device from the other in case some malicious user tries to insert a virus into the servers or legitimate users.
Q41. What do you mean by Ethernet?
Ethernet is a network technology used in LAN, MAN and WAN that connects devices using cables for the transmission of data. It provides services on the Physical and Data Link layers of the OSI Model.
Q42.What is SLIP?
SLIP stands for Serial Line Internet Protocol which allows a user to access the internet using the modem.
Q43. What is the difference between CSMA/CD and CSMA/CA?
| CSMA/ CD | CSMA/ CA |
The effect is after a collision | The effect is before a collision |
Minimizes the recovery time | Reduces the possibility of a collision |
Usually used in wired networks | Usually used in wireless networks |
Q44. Briefly explain what is tunnel mode?
Tunnel mode is used to encrypt the whole IP packet including the headers and the payload. It is basically used in a Site-to-Site VPN to secure communications between security gateways, firewalls, etc.
Q45. What do you mean by IPv6?
IPv6 stands for Internet Protocol version 6 and is the latest version of the Intenet Protocol. The IP address length is 128 bits which resolves the issue of approaching shortage of network addresses.
Q46. Explain the RSA algorithm briefly.
RSA is a cryptosystem used to secure data transmission named after Ron Rivest, Adi Shamir and Len Adleman. This algorithm has a public key for encryption while the decryption key is kept secure or private. The encryption key is created using two large prime numbers and is published along with an auxiliary value. Anybody can make use of this public key for encryption but only someone with the knowledge of the prime numbers can decrypt it. However, this algorithm is considered to be slow and for the same reason, it is not used very often to encrypt data.
Q47. What is an encoder?
An encoder is a program, circuit or a device that converts data from one format to another. Encoders convert analog signals into digital ones.
Q48. What is a decoder?
A decoder is a program, circuit or a device that converts the encoded data into its actual format. Decoders convert digital signals to analog ones.
Q49. What is sneakernet?
Sneakernet is the unofficial term for the transfer of electronic information by physically moving media which can be anything such as a Floppy disk, USB flash, optical disks, etc.
Q50. What are the components of a Protocol?
Protocols are a set of rules that govern communication. The key elements of a Protocol are as follows:
| Name | Description |
Syntax | Refers to the structure and format of data |
Semantics | Refers to the meaning of each portion of bits |
Timing | Refers to when data should be sent and received |
1. What is a Computer Network?
Ans: A computer network is a connection network between two or more nodes using Physical Media Links viz., cable or wireless in order to exchange data over pre-configured services and Protocols. A computer network is a collective result of – Electrical Engineering, Computer Science, Telecommunication, Computer Engineering and Information Technology involving their theoretical as well as practical aspects into action. The most widely used Computer Network of Today is Internet which supports World Wide Web (WWW).
2. What is DNS?
Ans: DNS stands for Domain Name System. It is a Naming System for all the resources over Internet which includes Physical nodes and Applications. DNS is a way to locate to a resource easily over a network and serves to be an essential component necessary for the working of Internet.
It is always easy to remember xyz.com that to remember its IP(v4) address 82.175.219.112. The condition gets more worse when you have to deal with IP(v6) address 2005:3200:230:7e:35dl:2874:2190. Now think of the scenario when you have a list of 10 most visited resource over Internet? Didn’t the things get more worse to remember? It is said and proved scientifically that humans are good in remembering names as compared to numbers.
The Domain Name System functions to assign Domain Names by mapping corresponding IP addresses and works in a Hierarchical and Distributed Fashion.
3. What are IPv4 and IPv6? Who manages these?
Ans: IPv4 and IPv6 are the versions of Internet Protocol which stands for Version4 and Version6 respectively. IP address is an unique value which represents a device over network. All the device over Internet must have a valid and Unique address to function normally.
IPv4 is a 32 bit numeric representation of devices over Internet, most widely used till date. It supports upto 4.3 billion (4,300,000,000) unique IP addresses. Seeing the continuing growth of Internet with more and more devices and users linking to Internet there was a need of better version of IP address which could support more users. Hence came IPv6 in 1995. An example of IPv4 is:
82.175.219.112
IPv6 is a 128 bit numeric representation of devices over Internet. It supports as much as 340 trillion, trillion, trillion (340,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000) unique IP address. This is sufficient to provide more than a billion of IP addresses to every human being on earth. Sufficient for centuries. With the invent of IPv6, we need not to bother about depleting Unique IP addresses. An example of IPv6 is:
2005:3200:230:7e:35dl:2874:2190
4. Give a brief description of PAN, LAN, HAN, SAN, CAN, MAN, WAN, GAN.
Ans: PAN stands for Personal Area Network. It is a connection of Computer and Devices that are close to a person VIZ., Computer, Telephones, Fax, Printers, etc. Range Limit – 10 meters.
LAN stands for Local Area Network. LAN is the connection of Computers and Devices over a small Geographical Location – Office, School, Hospital, etc. A LAN can be connected to WAN using a gateway (Router).
HAN stands for House Area Network. HAN is LAN of Home which connects to homely devices ranging from a few personal computers, phone, fax and printers.
SAN stands for Storage Area Network. SAN is the connection of various storage devices which seems local to a computer.
CAN stands for Campus Area Network, CAN is the connection of devices, printers, phones and accessories within a campus which Links to other departments of the organization within the same campus.
MAN stands for Metropolitan Area Network. MAN is the connection of loads of devices which spans to Large cities over a wide Geographical Area.
WAN stands for Wide Area Network. WAN connects devices, phones, printers, scanners, etc over a very wide geographical location which may range to connect cities, countries and ever continents.
GAN stands for Global Area Network. GAN connects mobiles across the globe using satellites.
5. What is POP3?
Ans: POP3 stands for Post Office Protocol Version3 (Current Version). POP is a protocol which listens on port 110 and is responsible for accessing the mail service on a client machine. POP3 works in two modes – Delete Mode and Keep Mode.
Delete Mode: A mail is deleted from the mailbox after successful retrieval.
Keep Mode: The Mail remains Intact in the mailbox after successful retrieval.
6. What is the criteria to check the network reliability?
Ans: A network Reliability is measured on following factors.
Downtime: The time it takes to recover.
Failure Frequency: The frequency when it fails to work the way it is intended.
7. What is a router?
Ans: A router is a physical device which acts as a gateway and connects to two network. It forwards the packets of data/information from one network to another. It acts as an interconnection Link between two network.
8. What are the use of cross and standard cables? Where do you find their usages?
Ans: A Network cable may be crossover as well as straight. Both of these cables have different wires arrangement in them, which serves to fulfill different purpose.
Area of application of Straight cable
Computer to Switch
Computer to Hub
Computer to Modem
Router to Switch
Ares of application of Crossover cable
Computer to Computer
Switch to Switch
Hub to Hub
9. What do you mean by Bandwidth?
Ans: Every Signal has a limit of its upper range and lower range of frequency of signal it can carry. This range of limit of network between its upper frequency and lower frequency is termed as Bandwidth.
10. What do you mean by MAC address? Does it has some link or something in common to Mac OS of Apple?
Ans: MAC stands for Media Access Control. It is the address of the device identified at Media Access Control Layer of Network Architecture. Similar to IP address MAC address is unique address, i.e., no two device can have same MAC address. MAC address is stored at the Read Only Memory (ROM) of the device.
MAC Address and Mac OS are two different things and it should not be confused with each other. Mac OS is a POSIX standard Operating System Developed upon FreeBSD used by Apple devices.
That’s all for now. We will be coming up with another articles on Networking series every now and then. Till then, don’t forget to provide us with your valuable feedback in the comment section below.














netflow
ReplyDeletesyslog
ping
active directory
bandwidth
virtualization
snmp
wmi
lpwa
rest
vpn
MQTT
packet sniffing
cctv
tls
iiot
server
cloud computing
IT professionals can start their career as Junior Programmer, Database Administrator, Junior Network Manager, Data Analyst, Software Developer, Software Engineer, and Client-Server Systems Manager, etc. Job openings for software professionals is much higher in the corporate sector than in public sector
Which IT technology is most in demand in 2022?
ReplyDeleteIT technology is most in demand in 2020 are Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning, Blockchain Technology, Cloud and Amazon Web Services (AWS), Cybersecurity, Data Science, Analytics and Visualization and Technology Skills Career Outlook.
Delete