Cloud || RAID || Data Storage and Backups || All Type Diskmgmt
A volume is a storage device, such as a fixed disk, floppy disk, or CD-ROM, that is formatted to store directories and files. A large volume can be divided into more than one logical volume, also called a partition
RAID Minimum HDD Required Raid Support
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Simple Volume 1 No
Spanned Volume min 2 max 32 No
Stripped Volume(RAID-0) 2 NO
Stripped With Parity Vol.(RAID-5) 3 Yes
Mirror Volume (RAID-1) 2 Yes
RAID 0+1 4 Yes
RAID 1+0 4 Yes
==============================================================
Storage :
FS - File System ???
ext2 - Extended V2 - Unix/Linux - outdated
ext3 - outdated
ext4 -RHEL 6 - limited in use
xfs - eXtended File System - RHEL 7 - max use in current days
FAT12 - File Allocation Table - outdated
FAT16 - maximum 4GB partition size support - outdated
FAT32 - Maximum storage 32 GB partition size support
NTFS V4.0 - New Technology File System - Outdated
NTFS 5. 0 - Current in process - Capacity - 2TB
ReFS - Resilient File System - 16EB
VMWare Storage - VMFS 5.0 = VMWare File System
Citix - ???
1024 Byte - 1KB
1024 Kilo Byte - 1MB
1024 Mega Byte - 1GB
1024 Giga Byte - 1 TB
1024 Tera Byte - 1 PB
1024 Peta Byte - 1 EB
1024 Exa Byte - 1 ZB
1024 Zeta Byte - 1 YB
1024 Yotta Byte -
File System:
1) MBR - Master Boot Record
- Maximum partition size support of 2TB.
- Maximum 4 Primary Partition supported.
2) GPT - GUID Partition Table (Global Unique ID)
- Maximum partition size support upto 18EB
- Maximum 128 Primary Partition supported.
Block Size - ???
Sector
HDD Connect ---> HDD Initialize ---> HDD Active ---> Partition ---> Format (FS Set) ---> Lable
diskmgmt.msc
fdisk /dev/sda
What is a System Reserve Patition?
MBR - Master Boot Record File storage which support to start the OS.
MBR Storage Size :
Windows 2000 Server - 8MB
Windows 2003 Server - 8 MB
Windows Server 2008 / R2 - 100MB
Windows Server 2012 / R2 - 350 MB
Windows Server 2016 RT - 500MB
Basic Disk:
- Maximum 4 Primary Partition supported.
- Not support for Redundancy.
- Support Maximum 2TB storage.
Dynamic Disk:
- Support for Redundancy.
- Support More than 2TB and upto 64TB.
Notice : Basic Disk can be converted into Dynamic Disk but
dynamic Disk cannot be converted into Basic disk.
HDD Types:
1) PATA = Parallel Advanced Technology Attachement / IDE(Integrated Drive Electronice)
PATA/IDE has 40 Pin Data Connection and 4 Pin Power Connector.
PATA/IDE HDD has 5600 RPM (Rotation Per Min)
2) SATA = Serial ATA
SATA has 7 Pin Data Connector and 15 Pin Power Connector.
SATA has 5600 and 7200 RPM max.
3) SCSI = Small Computer System Interface - Server only
4) SAS = Serial Attached SCSI - High Speed storage server
5) SSD = Solid State Drive - High Speed storage server
Desktop HDD Speed = 7200 RPM (Rotation per Min)
Laptop HDD Speed = 5400 RPM
SCSI HDD Speed = 12K, 16K upto 32000 RPM
IOPS = Input Output Per Second
Storage Types:
1) Magnatic Storage : FDD, HDD, Tape Drive (Avarage speed with average cost)
2) Optical Storage : CD, DVD, BluRay Disk (slow but less cost)
3) Flash Storage : Pendrive, Memory Card, SSD (Fast but costly)
JBOD = Just Bunch of Disk
RAID Minimum HDD Required Raid Support
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1)Simple Volume 1 No
You Set A Volume Size (Create A disk how many GB , TB )
Then You Assign The Drive letter (Any select )
File System select
YOU Use ExFAT
More Information
- Using the FORMAT command from the command line without specifying a cluster size.
- Formatting a volume from Windows Explorer when the Allocation Unit box in the Format dialog box lists Default Allocation Size.
By default, the maximum cluster size for NTFS under Windows NT 4.0 and later versions of Windows is 4 kilobytes (KB). This is because NTFS file compression is not possible on drives that have a larger cluster size. The format command won't use clusters larger than 4 KB unless the user specifically overrides the default settings. You can do this by using the /A: switch together with the Format command or by specifying a larger cluster size in the Format dialog box in Windows Explorer.
When you use the Convert.exe utility to convert a FAT partition to NTFS, Windows always uses the original FAT cluster size as the NTFS cluster size for cluster sizes up to 4 KB. If the FAT cluster size is greater than 4 KB, then the clusters are converted down to 4 KB in NTFS. This is because the FAT structures are aligned on cluster boundaries. Therefore, any larger cluster size would not allow for the conversion to function. Note also when formatting a partition under Windows NT 3.5, 3.51, and 4.0 Setup, the partition is first formatted to FAT and then converted to NTFS, so the cluster size will also always be as described earlier when a partition is formatted in Setup.
Default cluster sizes for NTFS
The following table describes the default cluster sizes for NTFS.| Volume size | Windows NT 3.51 | Windows NT 4.0 | Windows 7, Windows Server 2008 R2, Windows Server 2008, Windows Vista, Windows Server 2003, Windows XP, Windows 2000 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 7 MB–512 MB | 512 bytes | 4 KB | 4 KB |
| 512 MB–1 GB | 1 KB | 4 KB | 4 KB |
| 1 GB–2 GB | 2 KB | 4 KB | 4 KB |
| 2 GB–2 TB | 4 KB | 4 KB | 4 KB |
| 2 TB–16 TB | Not Supported* | Not Supported* | 4 KB |
| 16TB–32 TB | Not Supported* | Not Supported* | 8 KB |
| 32TB–64 TB | Not Supported* | Not Supported* | 16 KB |
| 64TB–128 TB | Not Supported* | Not Supported* | 32 KB |
| 128TB–256 TB | Not Supported* | Not Supported* | 64 KB |
| > 256 TB | Not Supported | Not Supported | Not Supported |
Note The asterisk (*) means that it is not supported because of the limitations of the master boot record (MBR).
Default cluster sizes for FAT16
The following table describes the default cluster sizes for FAT16.| Volume size | Windows NT 3.51 | Windows NT 4.0 | Windows 7, Windows Server 2008 R2, Windows Server 2008, Windows Vista, Windows Server 2003, Windows XP, Windows 2000 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 7 MB–8 MB | Not supported | Not supported | Not supported |
| 8 MB–32 MB | 512 bytes | 512 bytes | 512 bytes |
| 32 MB–64 MB | 1 KB | 1 KB | 1 KB |
| 64 MB–128 MB | 2 KB | 2 KB | 2 KB |
| 128 MB–256 MB | 4 KB | 4 KB | 4 KB |
| 256 MB–512 MB | 8 KB | 8 KB | 8 KB |
| 512 MB–1 GB | 16 KB | 16 KB | 16 KB |
| 1 GB–2 GB | 32 KB | 32 KB | 32 KB |
| 2 GB–4 GB | 64 KB | 64 KB | 64 KB |
| 4 GB–8 GB | Not supported | 128 KB* | Not supported |
| 8 GB–16 GB | Not supported | 256 KB* | Not supported |
| > 16 GB | Not supported | Not supported | Not supported |
Default cluster sizes for FAT32
The following table describes the default cluster sizes for FAT32.| Volume size | Windows NT 3.51 | Windows NT 4.0 | Windows 7, Windows Server 2008 R2, Windows Server 2008, Windows Vista, Windows Server 2003, Windows XP, Windows 2000 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 7 MB–16MB | Not supported | Not supported | Not supported |
| 16 MB–32 MB | 512 bytes | 512 bytes | Not supported |
| 32 MB–64 MB | 512 bytes | 512 bytes | 512 bytes |
| 64 MB–128 MB | 1 KB | 1 KB | 1 KB |
| 128 MB–256 MB | 2 KB | 2 KB | 2 KB |
| 256 MB–8GB | 4 KB | 4 KB | 4 KB |
| 8GB–16GB | 8 KB | 8 KB | 8 KB |
| 16GB–32GB | 16 KB | 16 KB | 16 KB |
| 32GB–2TB | 32 KB | Not supported | Not supported |
| > 2TB | Not supported | Not supported | Not supported |
Default cluster sizes for exFAT
The following table describes the default cluster sizes for exFAT.| Volume size | Windows 7, Windows Server 2008 R2, Windows Server 2008, Windows Vista, Windows Server 2003, Windows XP |
|---|---|
| 7 MB–256 MB | 4 KB |
| 256 MB–32 GB | 32 KB |
| 32 GB–256 TB | 128 KB |
| > 256 TB | Not supported |

=========================================================
RAID Minimum HDD Required Raid Support
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
2) Spanned Volume min 2 max 32 No
Spanned volume allows users to get more data on the disk without using mount points. By combining the multiple unallocated spaces of physical disks into a spanned volume, users can release drive letters for other uses and create a large volume for file system use.
mini 2 disk needed Then Next batten Show

===============================================================
RAID Minimum HDD Required Raid Support
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
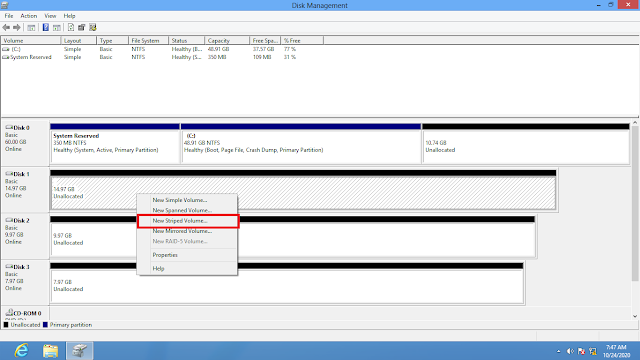
3) Stripped Volume(RAID-0) 2 NO
Data that is written to a striped volume is interleaved to all disks at the same time instead of sequentially. Therefore, disk performance is the fastest on a RAID 0 volume as compared to any other type of disk configuration. Administrators prefer to use striped volumes when input/output (I/O) speed is important
==============================================================
RAID Minimum HDD Required Raid Support
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Mirror Volume (RAID-1) 2 Yes









































IT professional can also get jobs in many public sector firms. Some of the leading public sector firms are BSNL, ISRO, CDIT, CDAC, etc. However, opportunities in public sector is far less than private sectors
ReplyDeleteFirewall information
VMware in Ubuntu
firewall Question
Server questions
Networkin questions
NLB
Disk type
Hyper-v Network
Virtual disk
shortcut Key CMD
RAID
Server in Install ADDS Roles
Is Information Technology a good course to study?
ReplyDeleteYes, as there are many great career opportunities associated for graduates of degree programs in Information Technology with great career opportunities.
Deletewindows 11
ReplyDeletehttps://drive.google.com/drive/folders/1_Grd5OTkx3KKqa0hGy-71eR49h0jXXhK?usp=drive_link